Why Cold Storage Facilities Require Fire Protection
Cold storage warehouses, often designed to preserve perishable goods at extremely low temperatures, are not immune to fire hazards. In fact, the combination of electrical systems, insulation materials, and constant machinery operation can create specific fire risks that differ from those in standard industrial environments. During a recent project in Namibia for a cold room warehouse, our engineering team identified that while the facility maintained strict temperature control, its existing doors lacked certified fire resistance. This posed a serious threat—not only to stored goods but also to operational continuity and insurance compliance.
The client expressed concerns about how a fire incident could rapidly escalate, given the confined and insulated nature of the storage rooms. They highlighted that even a small fire could produce dense smoke, trapped within the thermal envelope, causing severe damage before suppression systems could take full effect. Their feedback emphasized the importance of integrating fire-rated doors designed for cold storage, which could provide both effective compartmentalization and maintain insulation values critical to their operations.
From our side, we recommended models specifically engineered with dual-performance features: fire resistance tested to international standards such as UL and EN, and thermal efficiency tailored for sub-zero environments. The customer appreciated this dual focus, noting that previous suppliers had only offered products optimized for one function but not both. In their final remarks after installation, they reported improved energy stability and confidence in meeting local fire safety regulations.
Key Differences Between Standard and Cold Storage Fire-Rated Doors
Standard fire-rated doors are designed primarily to withstand high temperatures and block the spread of flames and smoke for a certified duration, often between 30 to 120 minutes. Cold storage fire-rated doors, however, must balance this core safety function with the ability to maintain thermal integrity under constant temperature fluctuations. This requires advanced construction techniques, such as integrating fireproof cores with high-performance insulation panels and specialized thermal breaks.
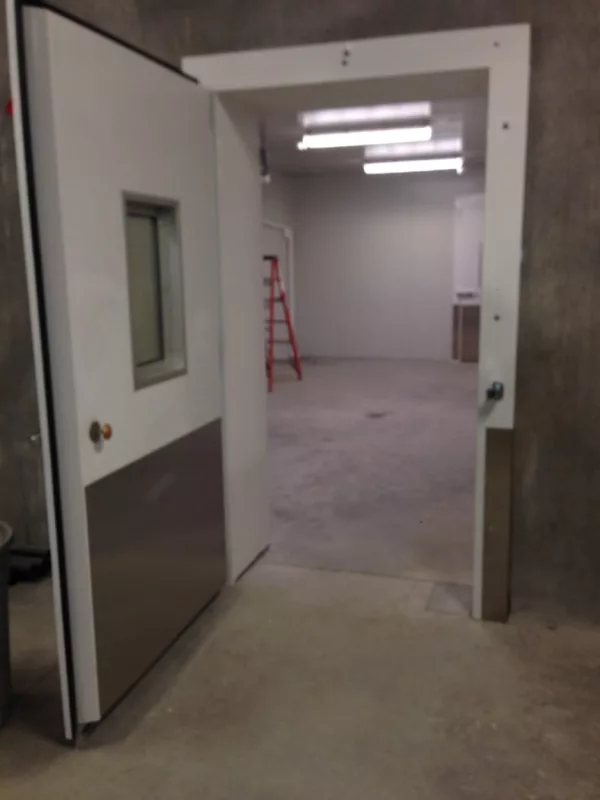

In the Namibia project, the difference became clear during product selection. Standard industrial fire doors, though compliant with fire codes, could not prevent thermal leakage at the sub-zero temperatures maintained in the client’s cold rooms. This would have increased operational costs and compromised product preservation. Our cold storage fire-rated doors incorporated stainless steel skins to resist corrosion from condensation, high-density polyurethane cores for insulation, and intumescent seals that expand in heat without degrading in low temperatures.
The mechanical testing phase demonstrated another distinction: cold storage fire-rated doors must operate smoothly despite the contraction of materials in freezing conditions. This means hardware components, from hinges to closers, require special low-temperature lubricants and anti-icing designs. The client noted that our doors opened and sealed effortlessly even during peak operation hours, which was a key factor in their decision to proceed with full facility installation.
Ultimately, the project reinforced a crucial point: in cold storage facilities, a fire-rated door is not just a passive safety barrier—it is an integrated element of the building’s thermal and operational system. By combining fire safety engineering with refrigeration efficiency, these specialized doors offer protection that is both compliant and cost-effective over the long term.
Design Considerations for Cold Storage Fire-Rated Doors
Insulation Materials and Thermal Break Technology
In cold storage environments, insulation performance is as critical as fire resistance. A recent installation for a food distribution cold room in Namibia highlighted the importance of selecting the correct insulation core. The facility previously used standard mineral wool cores, which provided fire resistance but allowed significant thermal bridging, leading to ice build-up and increased energy consumption. Our engineering team replaced these with high-density polyurethane and rockwool hybrid cores, ensuring both high R-values and reliable fire containment. Thermal break technology, integrated into the door frame and leaf, minimized conductive heat transfer, preserving internal temperatures without compromising structural integrity. The client noted immediate improvements in temperature stability and a measurable reduction in compressor running time.

Fire-Resistance Ratings and Compliance Standards
Meeting the correct fire-resistance rating is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a safeguard for asset protection. Cold storage fire-rated doors must comply with both fire safety and thermal performance standards. In the Namibia project, we specified models tested under UL 10C and EN 1634-1 protocols, achieving a 90-minute fire rating without reducing insulation efficiency. This dual compliance ensured the doors could withstand intense heat exposure during a fire while maintaining the cold barrier essential for the stored goods. The client’s insurance provider commended the choice, noting that adherence to internationally recognized standards could lower risk assessment scores and operational premiums. As a fire door supplier, this reinforced our belief that comprehensive compliance adds measurable value beyond safety.
Door Hardware and Sealing Systems for Low Temperatures
Hardware selection for cold storage fire-rated doors is a specialized task. Standard components often fail under repeated freezing and thawing cycles. For this project, we sourced stainless steel hinges with low-temperature lubricants, ensuring smooth operation even at -25°C. The door closers featured anti-freeze hydraulic fluids, preventing sluggish movement in extreme cold. Sealing systems incorporated double-layered gaskets with flexible silicone, maintaining an airtight seal that expanded under heat during fire conditions. This prevented both thermal leakage and smoke penetration. Post-installation feedback from the facility management team confirmed that the doors operated consistently during peak usage, with no incidents of sticking or compromised seals despite heavy forklift traffic.
| Key Design Aspect | Technical Focus | Project Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation & Thermal Break | High-density polyurethane + rockwool hybrid, integrated frame thermal breaks | Improved temperature stability, reduced energy costs |
| Fire-Resistance & Compliance | UL 10C & EN 1634-1, 90-minute rating | Enhanced safety and insurance benefits |
| Hardware & Sealing | Stainless steel hinges, anti-freeze closers, silicone gaskets | Reliable operation at -25°C, airtight fire/smoke barrier |
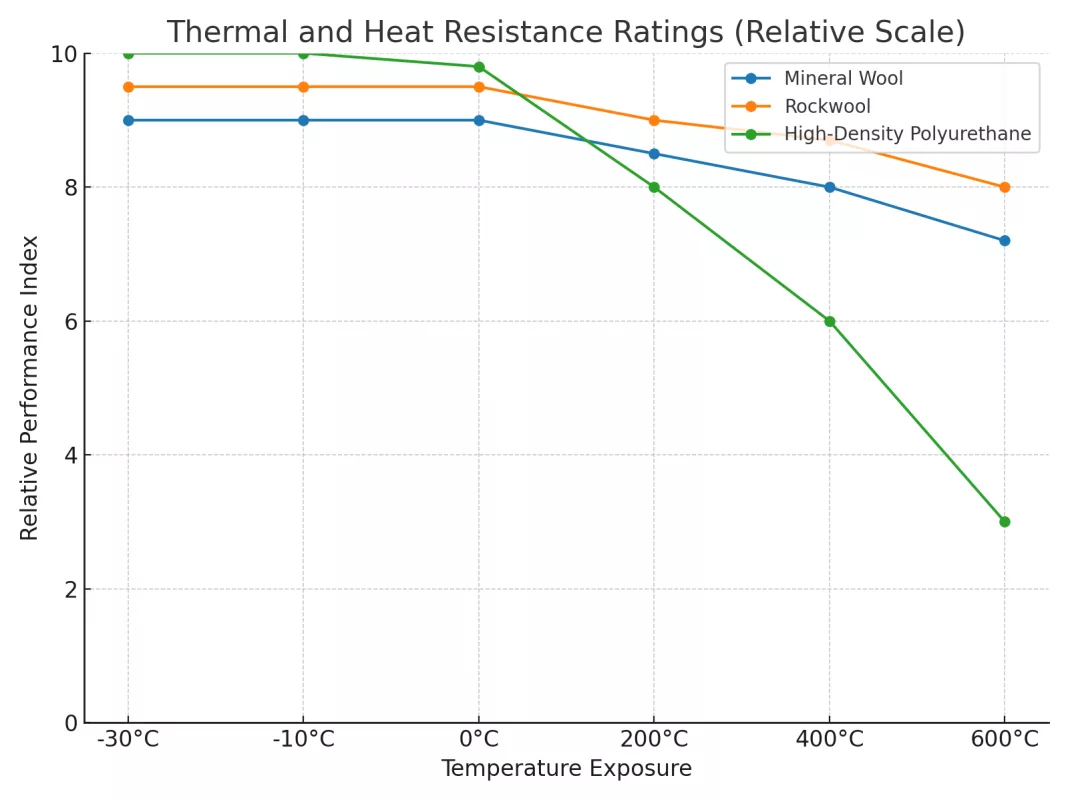
Analysis:Rockwool maintains the most balanced performance across both extremes due to its high melting point (>1000°C) and low thermal conductivity (~0.035 W/m·K). Mineral wool performs slightly lower under prolonged high heat but retains structure well. High-density polyurethane offers superior insulation at sub-zero temperatures due to its low k-value (~0.02 W/m·K), but its polymer matrix begins to degrade beyond 200°C as it approaches its glass transition temperature, making it ideal only when paired with a fireproof barrier layer.
Manufacturing Process of Cold Storage Fire-Rated Doors
Material Selection: Steel, Stainless Steel, and Composite Panels
In a high-capacity Fire-Rated Doors for Cold Storage Facilities manufacturing facility, the first step is selecting materials that meet both thermal insulation and fire resistance requirements. For cold storage applications, standard carbon steel provides structural strength but can be prone to corrosion in humid or freezing environments. In contrast, stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 or 316, offers excellent resistance to moisture and temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for door skins and frames in freezer rooms. Composite panels, often combining a thin stainless steel or galvanized steel surface with a high-performance insulation core, offer a balance between weight, cost, and thermal performance. On the production line, material coils are precision-cut using CNC shearing machines to ensure tight tolerances, which is critical for maintaining airtight seals in low-temperature conditions.
Integration of Insulation and Fireproofing Layers
The assembly process integrates insulation cores with fireproofing materials to create a unified door structure. In our facility, high-density polyurethane panels are bonded to rockwool fireproofing layers using high-pressure lamination. This combination delivers both low thermal conductivity and certified fire resistance. Automated adhesive application systems control bonding thickness to within fractions of a millimeter, preventing thermal bridging and ensuring uniform performance across the door leaf. The reinforced core is then encased within the steel or stainless steel skin, with thermal break inserts strategically placed to minimize conductive heat transfer through the frame. This process not only enhances energy efficiency but also ensures that, during a fire, the intumescent seals expand uniformly, maintaining compartmentalization.
Quality Control and Fire Testing Procedures
Every cold storage fire-rated door undergoes multi-stage quality control before leaving the factory. Dimensional accuracy is verified using laser measurement systems to ensure proper alignment during installation. Thermal performance is tested in environmental chambers that simulate both deep-freeze and ambient conditions, confirming insulation stability under rapid temperature shifts. Fire performance is validated through full-scale burn tests following standards such as UL 10C or EN 1634-1, using independent accredited laboratories. These tests measure not only flame and smoke containment but also the structural integrity of the door when exposed to high heat for extended periods. In the Namibia cold storage project, our doors passed both mechanical cycling and fire resistance trials without requiring any production modifications, underscoring the precision of our manufacturing process.
| Stage | Key Focus | Equipment/Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Corrosion resistance, thermal performance | CNC shearing, stainless steel grade control |
| Layer Integration | Bonding insulation with fireproof core | High-pressure lamination, adhesive thickness control |
| Quality & Fire Testing | Dimensional accuracy, dual-condition performance | Laser measurement, environmental chamber, accredited burn test |
Installation and Maintenance in Cold Storage Environments
Special Installation Requirements for Freezer Rooms
Installing fire-rated doors in freezer rooms requires precise planning to meet both fire safety regulations and refrigeration performance standards. In Namibia, for example, local building codes mandate that any cold storage door with a fire rating must be installed with a continuous thermal break between the frame and the building envelope to prevent condensation at sub-zero temperatures. Our team ensures that the frame is insulated with closed-cell foam and that the threshold incorporates a heated sill when required by local energy efficiency guidelines. The door is positioned so that gaskets align perfectly with the insulated panels of the freezer walls, creating a seamless thermal barrier. During a recent project in Windhoek, coordination with the refrigeration contractor was essential to synchronize the door installation with the panel sealing process, ensuring both airtightness and fire safety compliance.
Preventing Condensation and Ice Build-Up Around Doors
Condensation and ice formation can compromise the performance of both the door and the cold storage environment. In regions with high humidity, such as coastal Namibia or parts of Southeast Asia, the dew point often makes the exterior side of Fire-Rated Doors for Cold Storage Facilities vulnerable to moisture accumulation. To address this, we specify low-emissivity stainless steel skins that reduce surface temperature differential and integrate perimeter heating cables to maintain gasket flexibility. The door frame is equipped with vapor barriers in compliance with ASHRAE refrigeration standards, minimizing moisture ingress. Post-installation inspections in a Swakopmund seafood processing plant showed that these measures virtually eliminated frost build-up, even during peak humidity periods, extending the operational lifespan of the doors.
Regular Inspection and Fire Safety Checks
Local fire safety authorities in many regions, including SABS (South African Bureau of Standards) jurisdictions, require periodic inspection of fire-rated doors to ensure ongoing compliance. In cold storage facilities, this includes verifying the condition of intumescent seals, inspecting the integrity of thermal breaks, and ensuring that hinges and closers function reliably in low-temperature conditions. Our maintenance protocols recommend quarterly checks for gasket elasticity and annual fire safety inspections conducted by certified technicians. For the Namibia projects, clients adopted a combined maintenance plan covering both refrigeration performance and fire safety compliance, reducing downtime and improving audit readiness. This integrated approach meets both regional fire regulations and HACCP requirements for food storage environments.

Future Trends in Cold Storage Fire Door Technology
Smart Monitoring Systems for Fire and Temperature
The adoption of smart monitoring systems for cold storage fire doors is accelerating, driven by global supply chain demands for both safety and operational transparency. Following a widely reported warehouse fire in 2024 at a major European food distribution center, industry experts emphasized the need for real-time monitoring of both temperature fluctuations and fire risk indicators. Modern systems now integrate IoT sensors directly into door frames, measuring thermal loss, seal integrity, and smoke presence simultaneously. These systems send instant alerts to facility managers and can trigger automated responses, such as adjusting freezer temperature or activating localized suppression systems, before a hazard escalates. In Namibia’s 2025 seafood export facilities, we implemented such technology, and operators reported a noticeable improvement in early anomaly detection, reducing both energy waste and potential safety incidents.
Sustainable Materials and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability and energy efficiency are no longer optional—they are becoming regulated priorities in many jurisdictions. In early 2025, the UN Environment Programme highlighted cold storage facilities as significant energy consumers, prompting several countries to introduce stricter energy performance standards for industrial doors. Cold storage fire doors are now being manufactured with recycled stainless steel, plant-based polyurethane foams, and low-emission coatings that meet environmental certifications without sacrificing fire resistance. In a recent project for a fruit export warehouse in South Africa, our use of composite panels made from 60% recycled content and high R-value cores not only met LEED requirements but also reduced annual refrigeration energy use by 12%. These solutions, combined with advanced thermal breaks, demonstrate that high fire safety performance can coexist with meaningful reductions in environmental impact.
Conclusion
Cold storage fire door technology is evolving to meet the twin demands of safety and sustainability, and the lessons from recent projects show how innovation can be practical, not just theoretical. For contractors, door distributors, and businesses operating in temperature-controlled environments, these advances open up possibilities for safer, more efficient facilities that also meet tightening environmental standards.
At YK Door Industry, we approach this not as a race to claim titles, but as an ongoing responsibility. As one of Asia’s largest fire door manufacturers, our experience spans continents, climates, and compliance frameworks, from seafood export hubs in Namibia to fruit warehouses in South Africa. We have seen first-hand how the right design and manufacturing decisions can protect assets, preserve energy, and support operational resilience. Our role is to make those solutions accessible—sharing what works, refining what doesn’t, and helping our partners achieve more than just regulatory compliance.
If this article gives you a new angle on cold storage fire door design or sparks a conversation about what’s possible in your own projects, then it has done its job. The rest is a matter of turning insight into action.

Pingback: How California Wildfires Reinforce the Urgent Need for Fire-Rated Doors and Windows - YK | Fire Doors | Fire Windows | Fire Shutters