Steel Fireproof Door Compliance with GB 12955-2008 Standards
An Industry Perspective from YK Fire Rated Door Manufacturer
The adoption of hot-dip galvanized steel sheets in the manufacturing of steel fireproof doors has become increasingly widespread in China—thanks to their outstanding corrosion resistance, attractive finish, and adaptability for post-processing. These attributes, coupled with cost-efficiency and low environmental impact, make this material a preferred choice for constructing high-performance metal fire doors, stainless steel fire doors, and other variants used across industrial and commercial settings.
Evolving Production of Galvanized Steel in China
Between the 1950s and 1970s, China installed around 15 solvent-based hot-dip galvanizing lines, collectively producing about 100,000 tons annually. These lines primarily relied on hot-rolled, pickled plates. However, the limitations were significant: inconsistent product quality, elevated operational costs, and considerable environmental hazards. As a result, they were gradually decommissioned in the 1980s.
The shift toward modernization began in 1979 when Wuhan Iron and Steel Corporation brought in China’s first continuous hot-dip galvanizing line from Germany. With a 150,000 t/a capacity, this move laid the groundwork for large-scale industrial transformation. By the early 1990s, continuous galvanizing had entered a period of rapid expansion. Eleven production lines were operational nationwide, with an annual output reaching 1.82 million tons—about 2% of the country’s total steel production.
This industrial evolution directly influenced the steel fire resistance door sector. As demand grew for commercial doors capable of meeting stringent safety and durability standards, the reliance on advanced galvanizing technologies became indispensable. In response, leading state-owned steel enterprises—including Pangang, Baosteel, and Ansteel—invested heavily in next-generation galvanizing units. Most of these facilities boasted imported technologies, state-of-the-art equipment, and annual outputs ranging from 350,000 to 500,000 tons. Their target markets included automotive manufacturing, premium construction materials, and home appliances—industries where high-precision, corrosion-resistant materials are non-negotiable.
For manufacturers like YK fire rated door manufacturer, this surge in material quality and availability has enabled the production of next-generation steel fire doors that align with GB 12955-2008 standards. These enhanced materials now form the backbone of doors used in complex industrial environments, ensuring both regulatory compliance and long-term performance.

Private Sector Contributions and Technological Evolution in Galvanized Steel for Fireproof Doors
While major state-owned enterprises led early investments in large-scale galvanizing infrastructure, the private sector also played a decisive role in expanding China’s galvanized steel capacity. A number of independent galvanizing units were established by private companies—many of them rooted in steel trading—with a strong understanding of raw material sourcing and a broad downstream network. These firms often leveraged their operational agility and deep market insight to remain competitive, even when relying predominantly on domestic technology and equipment. Units typically ranged between 100,000 and 150,000 tons annually and catered largely to the general construction and commercial door markets.
Some well-funded entrepreneurs built entire cold rolling operations to support their galvanizing lines. Although their investment levels were lower than those of large state-owned entities, their products—often used in manufacturing metal fire doors and other general-purpose steel items—offered compelling value and accessibility.
By the close of 2005, over 40 high-capacity hot-dip galvanizing lines had been established by China’s state-owned enterprises and their joint ventures, boasting a combined capacity of over 15 million tons per annum (t/a). Private enterprises, on the other hand, had installed more than 80 galvanizing units, totaling a comparable output. In terms of scale, the private sector kept pace. However, state-owned steelmakers maintained an edge in product quality, technical sophistication, and supply chain stability—factors crucial for manufacturers like YK fire rated door manufacturer, where premium inputs are essential for reliable steel fire resistance doors.
Industrial Growth Reflected in National Production Data
Data from the China Iron and Steel Industry Association underscores the momentum: between 1999 and 2004, China’s galvanized sheet output rose from 1.45 to 4.17 million tons, with an average annual growth rate of 23.5% (excluding private sector production). Imports initially surged, growing by 37.3% annually until 2003, before dropping to 4.35 million tons in 2004—a decline of over a million tons, indicating improving domestic self-sufficiency.
Exports told a similar story. Annual outbound shipments hovered around 81,000 tons until 2004, when they unexpectedly jumped to 522,000 tons. The first quarter of 2005 continued the trend: galvanized steel production rose by nearly 40% year-on-year, while imports fell 31%, and exports increased 11.8%. Clearly, the sector was shifting from rapid growth to global competitiveness, paving the way for broader adoption of galvanized materials in stainless steel fire door applications and high-performance commercial fireproof doors.
Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Technology: Eight Key Trends
Technological developments in hot-dip galvanizing have further strengthened the material foundation for fire-rated steel doors, especially those requiring compliance with GB 12955-2008 standards. Key industry trends include:
1. Higher Production Capacity
Post-1990s, galvanizing lines with over 300,000 t/a capacity became standard globally, exceeding 28 million t/a in total capacity. China followed this trajectory, supporting high-volume, high-quality steel sheet production vital for large-scale steel fire door manufacturing.
2. Specialized Processing Lines
Dedicated lines emerged for different applications—automotive versus building materials—leading to process optimization, reduced costs, and improved yield.
3. Surface Cleanliness Prioritization
Modern automotive sheet units adopted alkaline electrolytic cleaning and full-radiant tube heating. Even lower-cost commercial door-grade materials now benefit from upgraded Sendzimir lines that include robust surface cleaning sections.
4. Adoption of Tower Furnaces
Though costlier, tower furnaces offer better gas sealing, reduced roll maintenance, and consistent plate shaping—advantages increasingly favored even by mid-capacity producers. These furnaces are now commonplace in both international and Chinese galvanizing operations.
5. Enhanced Furnace Efficiency
New designs reclaim exhaust heat, minimize deformation, and integrate advanced burners to ensure even temperature control. These enhancements result in lower NOx emissions and greater environmental sustainability—an important factor for fireproof door manufacturers focused on green building compliance.
6. Upgraded Galvanizing Equipment-Steel fireproof door compliance
Air knives now feature precise strip tracking, stable positioning, and automatic lip cleaning. Zinc pot innovations, including ceramic linings and coreless designs powered by electromagnetic sealing, extend service life and eliminate corrosion-prone components.
7. Superior Leveling Systems
Four-roll and tension levelers, used in combination, allow precise control over elongation and finish quality. This is crucial for applications such as metal fire doors requiring smooth, uniform surfaces and dimensional accuracy.
8. Advanced Post-Treatment Options
Finishing treatments—including passivation, phosphating, and eco-friendly coatings—improve corrosion resistance and meet varied client needs. Chromium-free alternatives like ACM solutions have shown promise in replacing traditional chromates, reducing toxicity without sacrificing performance.
For YK and other forward-looking manufacturers, these improvements in galvanized steel production and treatment technologies are pivotal. They not only ensure compliance with fireproofing standards but also enhance product durability and market competitiveness across the fire-rated commercial door segment.
Zinc Alloy Coatings and Fire Door Durability
The advancement of zinc alloy-coated steel sheets has brought significant improvements over conventional galvanized steel, both in corrosion resistance and structural stability—attributes critical for long-lasting fire-rated doors. Alloys such as aluminum-zinc (Galvalume), zinc-aluminum (Galfan), and zinc-iron (Galvanneal) have seen increased application across the industry. These materials, when used in steel fireproof door construction, offer improved resistance to oxidation, humidity, and chemical exposure—factors directly affecting fire compliance ratings in industrial and commercial installations.
Nisshin Steel’s development of the ZAM (zinc-aluminum-magnesium) alloy, which demonstrates corrosion resistance up to ten times higher than standard galvanized coatings, represents a milestone in material science. The use of such high-performance coatings in fire rated metal doors enhances their ability to maintain integrity under extreme conditions.
Enhancing Material Performance for Fire Door Applications
Aluminum-zinc and zinc-aluminum alloys are widely adopted in building and light industrial applications for their superior corrosion resistance, formability, and adherence to paint layers—essential features for steel fire doors requiring both functional and aesthetic endurance. In contrast, zinc-iron coatings, typically used in automotive manufacturing, provide enhanced weldability and post-paint corrosion resistance, making them ideal candidates for customized fire rated stainless steel doors in high-performance scenarios.
To support the diverse coating needs of modern fireproof steel structures, galvanizing units have evolved. Features such as dual galvanizing pots with mobility functions now enable quick switching between alloy types, which ensures consistent quality across batches of commercial-grade steel fire doors. Additionally, technologies like the coreless zinc pot, introduced by Applied Materials, have optimized energy use and production efficiency—an important factor for large-scale fire door manufacturing.
Spangle-Free Sheets and Environmental Considerations
With growing environmental awareness and evolving industry standards, fire-rated commercial doors are increasingly made from spangle-free, lead-free steel sheets. These materials not only reduce intergranular corrosion—extending the service life of doors in harsh environments—but also align with stricter environmental regulations. European manufacturers have already moved away from traditional spangled steel sheets, setting a precedent that is now echoed by responsible producers like YK.
Ultra-Deep Drawing and High-Strength Steel in Fire Door Construction
In producing steel fire doors for high-risk environments such as industrial warehouses or data centers, structural integrity is non-negotiable. High-strength galvanized steel sheets, including those capable of ultra-deep drawing, play a central role here. Despite challenges posed by high-silicon and manganese content (which hinder zinc adhesion), chemical innovations—such as molybdenum alloying—have enabled the development of dual-phase and TRIP steels suitable for fire-resistant applications.
Addressing Fireproof Door Demands Through Coating Precision-Steel fireproof door compliance
The demand for ultra-thin coatings, such as 25–30g/m², especially in the production of lightweight fire-resistant doors for electronic enclosures, continues to rise. Modern equipment like precision air knives now supports this demand, enabling manufacturers to produce galvanized sheets that meet strict dimensional and performance tolerances. These thin coatings can serve as a viable alternative to more costly tin-plated or electro-galvanized materials, without compromising on the structural standards required by international fire safety codes.
Cost Sensitivity and Market Regulation in the Galvanized Steel Industry: Implications for Fireproof Door Compliance
Minor Impact of Ore and Energy Price Increases on Coated Steel Sheets
Since 2004, global increases in ore and energy prices have influenced the cost structure of steel-related products. However, hot-dip galvanized steel sheets—commonly used in galvanized steel fire doors—have shown only moderate sensitivity to these fluctuations. As value-added, deeply processed materials, their pricing is less dependent on raw ore costs.
Moreover, the long-process production methods used for galvanized substrates, which contrast with short-process techniques reliant on scrap steel and electric furnaces, tend to be more energy-efficient. This helps mitigate the impact of energy price volatility. However, one key cost driver remains: the price of zinc ingots. As zinc is essential for corrosion protection in steel fireproof door manufacturing, any surge in its market price directly affects profitability across the metal fire door industry.
Reinforcing Compliance Through a Standardized Market Access System
Although China has established national product standards for hot-dip galvanized steel sheets used in the construction sector, enforcement remains inconsistent. A significant number of manufacturers produce commercial steel doors or structural materials without strictly following these standards. In particular, the reduction of zinc layer thickness to cut costs puts compliant companies at a disadvantage, distorts market competition, and increases long-term safety risks for end users.
To ensure quality and safety, especially for fire-rated outdoor metal doors, it is essential to implement a compulsory market access system. Products failing to meet national standards should be excluded from the market. This would protect both industry integrity and public safety, while promoting fair competition.
The galvanized steel industry must also improve self-regulation, align more closely with international standards, and embrace competition as a pathway to sustainable development—especially in applications where steel fireproof door compliance is mission-critical.
Manufacturing Process Overview: Galvanized Steel Fireproof Doors
Galvanized steel fire doors serve as a first line of defense in building fire protection systems. Combining the structural strength of steel with certified fire-resistant performance, these doors delay flame spread and safeguard evacuation routes. The following outlines the complete manufacturing process, highlighting quality control at each stage.
1. Material Selection and Procurement
- Steel Substrates: Cold-rolled or hot-rolled steel sheets with excellent mechanical properties are selected. All materials conform to national fire safety standards.
- Fireproof Core Materials: Non-combustible core options—such as perlite boards, vermiculite boards, or mineral fiber composites—are used to enhance fire resistance.
- Galvanizing Coatings: Sheets undergo hot-dip or electro-galvanizing processes to ensure anti-corrosion properties meet required thresholds.
- Hardware Components: Fire-rated hinges, door closers, locks, and seals are sourced from certified suppliers to ensure complete fireproof system performance.
2. Surface Galvanizing Process
- Pretreatment: Surfaces are degreased, deoxidized, and cleaned to eliminate impurities.
- Galvanizing: Zinc coating is applied through hot-dip or electroplating methods, forming a dense, even protective layer.
- Post-treatment: Zinc layers are inspected and corrected to eliminate defects and ensure uniformity.
3. Fireproof Core Integration
- Adhesives: High-temperature bonding agents are used to secure fire-resistant materials.
- Lamination: Steel sheets and core materials are compressed under controlled pressure to form a stable, fire-rated panel.
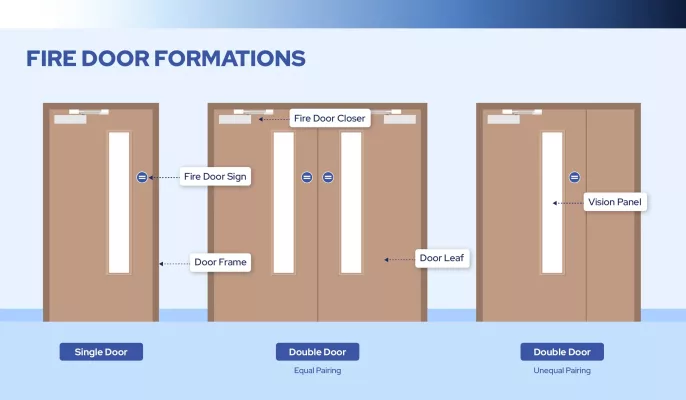
4. Door Frame and Leaf Fabrication
- Cutting and Forming: Galvanized steel is precisely shaped based on CAD drawings.
- Welding: High-quality welding techniques ensure structural durability and fireproof integrity.
- Surface Treatment: Post-weld grinding and polishing improve finish and prepare surfaces for coating.
5. Hardware Installation
- Marking and Drilling: Hardware mounting positions are accurately determined and drilled.
- Assembly: Certified components are installed to guarantee ease of use, security, and fire performance compliance.
6. Quality Inspection and Testing
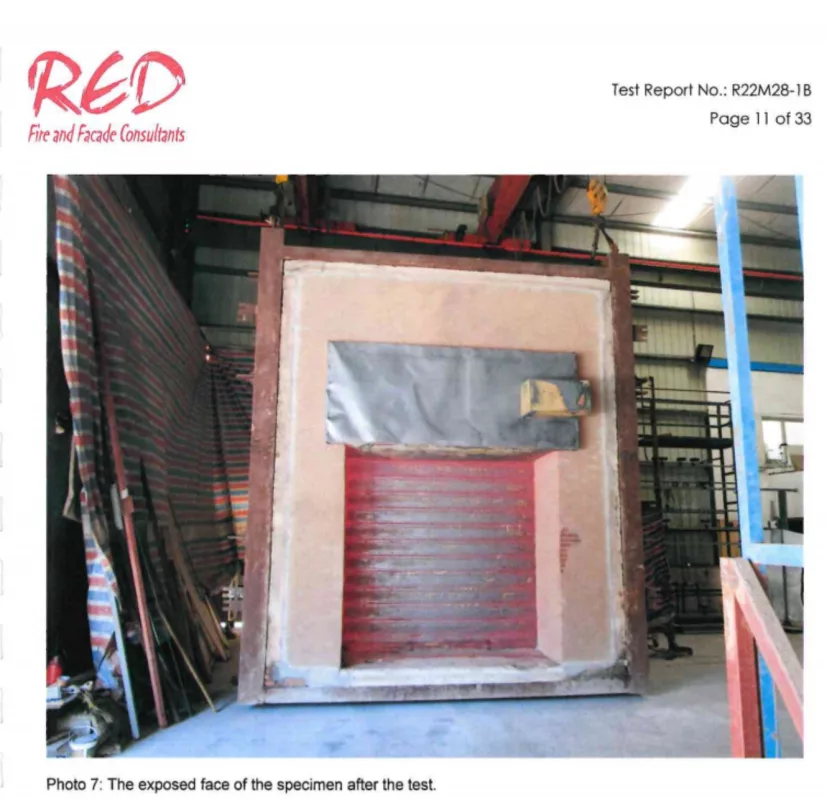
- Visual and Dimensional Checks: Surface smoothness and component dimensions are verified.
- Fire Resistance Testing: National-standard burn tests validate the fire rating of the assembled fire door system.
- Functional Testing: Hinges, locks, and closers are tested for operational reliability and sealing performance.
7. Surface Finishing and Coating
- Priming: Anti-rust primer enhances base corrosion resistance.
- Color Coating: High-temperature paint is applied in customer-specified or standard colors.
- Curing: Finished doors are placed in curing chambers to ensure adhesion strength and uniform finish.
8. Final Assembly and Packaging
Packaging: Moisture-proof and impact-resistant packaging safeguards the product during transport. Each fire-rated steel door is labeled and certified before shipment.
Door Assembly: Frames, leaves, and hardware are combined into a finished product.
Adjustment and Alignment: All mechanical elements are fine-tuned for proper operation.